Filtration
Filtration is the mechanical or physical process used to separate solids from liquid with the aid of an interposing medium (filter).
Turbidity reduction:
The method typically applied for turbidity reduction**
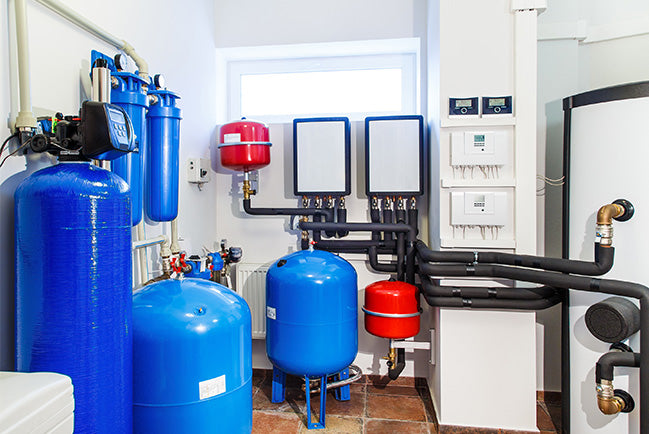
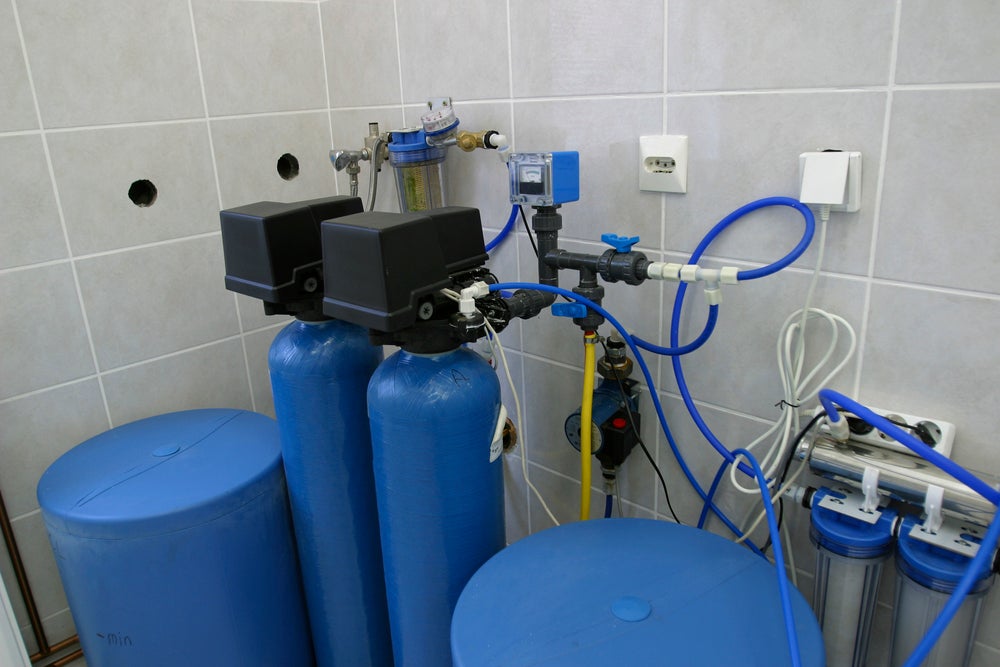
is media filtration: Filter media is placed in a media filter housing (e.g. a fibreglass filter vessel or a steel filter vessel – refer to pictures) and the water is then filtered inside of this filter.
Filter media for turbidity reduction:
- Glass media: Small particles of recycled glass used to capture sediment, dirt, rust and other particles from water.
Enhanced turbidity reduction:
There are two main ways to purify water with significantly high levels of turbidity: Disc filtration and ultrafiltration. These are often used together in a water treatment system.
- Disc filtration: Also known as screening, disc filtration offers depth filtration. It works by trapping particles between the discs and allowing the filtered water to pass through.
- Ultrafiltration: Ultrafiltration is pressure-driven purification process in which water is forced through an ultrafine membrane to remove contaminants completely, from suspended solids to bacteria and viruses.
**Turbidity: The cloudiness or haziness of a liquid, usually caused by a large numbers of individual particles like suspended matter or stirred-up sediment.
Turbidity reduction: Reducing turbidity by removing particles.
Metal removal:
Similar to turbidity reduction, media filtration is applied to remove metals – such as arsenic, iron or manganese –
from water. The process incorporates media that expediates the oxidation of dissolved metals within the filter bed, assisting in reducing costly chemistry and improving water quality.
Filter media for metal removal:
- Katalox: An advanced filtration media that removes metals and other contaminants from water. It’s composed of gamma manganese dioxide-coated Zeosorb (Zeosorb is another type of filter media made of zeolite).
- DMI: DMI-65 is a powerful silica sand-based catalytic water filter media that removes iron and manganese from water by dissolving them.
Organics and chlorine removal:
Media filtration is applied to remove chlorine and/or organics. The process however is one of adsorption rather than filtration.
Filter media for organic chlorine removal:
- Granular activated carbon (GAC): An adsorption
- media consisting of a hybrid mixture of a wide variety of graphite platelets interconnected by non-graphitic carbon bonding.



Filtration Benefits
-

Prevents Sediment in Appliances
-
Removes Known Toxins in Drinking Water
-

Improves Overall Wellbeing
-

Prevents Against Disease
-

Safe Water for Everyday Use
-
Removes water Impurities & Dangerous Contaminants such as Chlorine






